What is blepharospasm?
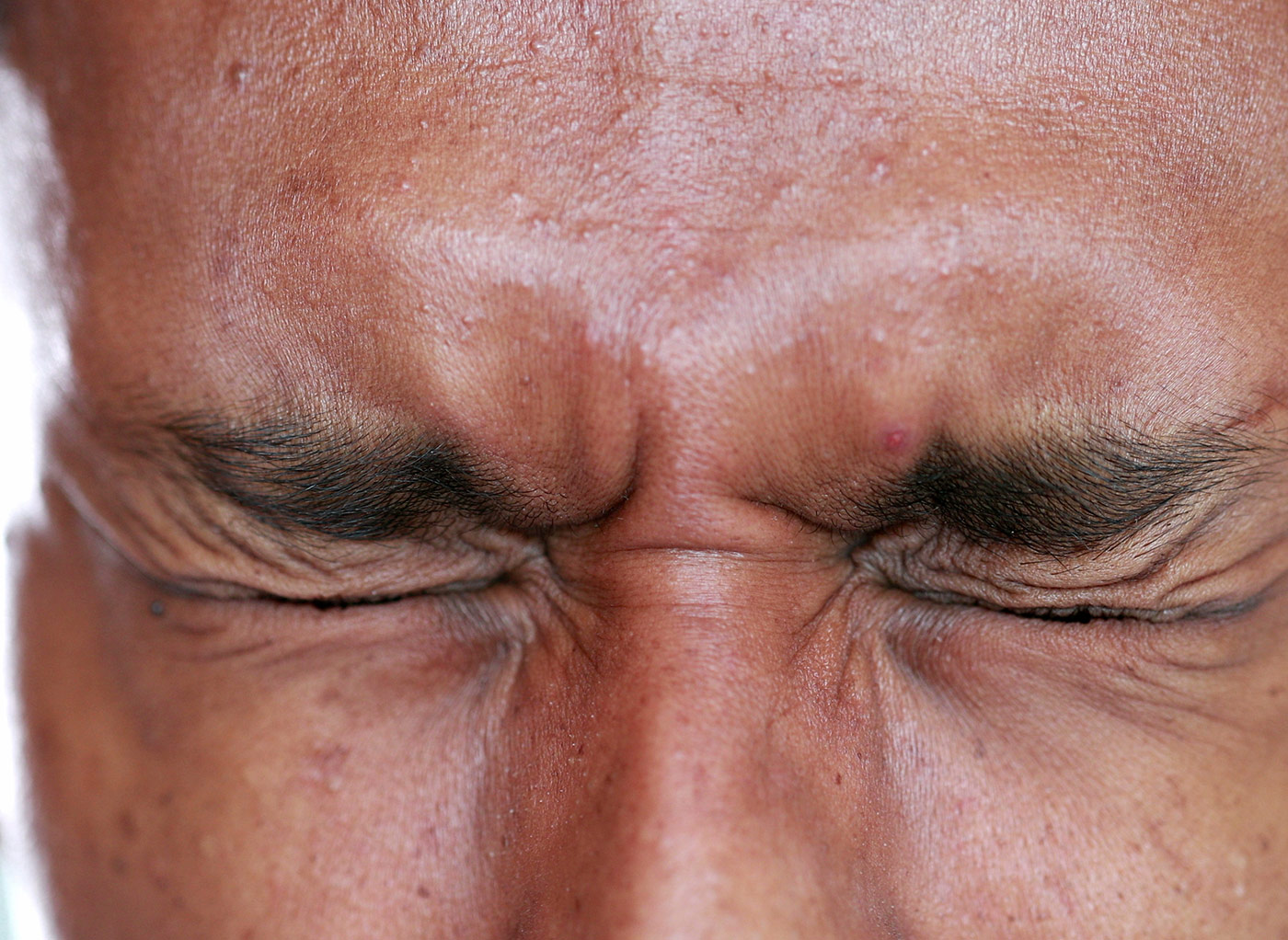
Blepharospasm is a term used to describe involuntary contraction of the eyelid muscles that leads to frequent, uncontrollable blinking. Blepharospasm often affects both eyelids, making it difficult to open the eyelids. In severe cases, this debilitating condition can lead to what is known as “functional blindness” because the patient is unable to open, or keep open, the eyelids for any significant period of time.
Approximately 75% of patients with blepharospasm are female and the average age at onset is 56 years. Although the exact cause of this disorder is unknown, experts believe that it may be caused by an inappropriate signal within the part of the brain known as the basal ganglia.
What are the symptoms of blepharospasm?
In the early stages of blepharospasm, symptoms include irritation and discomfort of the eyelids as well as an increase in blinking often associated with light and glare. There may be a feeling of dryness or a sensation of grittiness in the eyes. Symptoms may progress to more sustained eyelid closure that interferes with normal activities such as reading, walking and socialising. The degree of incapacity may vary from day to day. Some activities, such as driving a car, can become quite hazardous because of the inability to keep the eyelids open at will. Bright, dazzling or flickering lights, dusty or smoky air, or high-speed travel by train or car can make the symptoms worse.
What is the long-term outlook for blepharospasm?
The initial stages of sensitivity to glare and uncontrollable blinking may eventually disappear over the course of a few months. If the blepharospasm progresses, blinking usually becomes more frequent, forceful and uncontrollable. Sustained eyelid closure may develop. Symptoms fluctuate in severity so there may be periods when the symptoms are less troublesome.
What is hemifacial spasm?
Related to blepharospasm, hemifacial spasm is a neuromuscular disorder characterised by frequent involuntary contractions of the muscles on one side of the face. Hemifacial spasm is rare, affecting around 8 out of 100,000 men and 15 out of 100,000 women. Spasm affecting the left side is slightly more common than right-sided spasm.

What are the symptoms of hemifacial spasm?
The earliest symptom is usually an intermittent twitching of the eyelid muscle that can lead to forced closure of the eye. The spasm can spread gradually to involve the muscles of the lower face, which may cause the mouth to be pulled to one side. Eventually the spasms involve all of the muscles on one side of the face almost continuously. In some severe cases, the spasms may cause the mouth to become clamped shut, making speaking, eating, and swallowing difficult.
What causes hemifacial spasm?
In most people, there is no apparent cause for hemifacial spasm. Occasionally, it can be attributed to a facial nerve injury, pressure on the Vllth facial nerve or a tumour. Hemifacial spasm can also follow Bell’s palsy (an inflammation of the facial nerve resulting in temporary facial weakness) due to incorrect regeneration of the facial nerve.
What is botulinum toxin?
Botulinum toxin is a natural purified protein. The active ingredient is botulinum toxin type A which is extracted from bacteria under controlled laboratory conditions, similar to the way penicillin is produced from a mould. Botulinum toxin has been used in Australia in the management of blepharospasm and hemifacial spasm since 1993.
How does botulinum toxin work?
Normally, the brain sends electrochemical messages to the muscles via nerves to make them contract and move. These messages are transmitted from a nerve to the muscle by a substance called acetylcholine. When too much acetylcholine is released due to inappropriate messages from the central nervous system, the muscles become overly active and spasm or tighten up. Botulinum toxin temporarily blocks the nerve’s ability to release acetylcholine. As a result, the muscle spasms stop or are greatly reduced, providing relief from symptoms.

The Botulinum Toxin Process
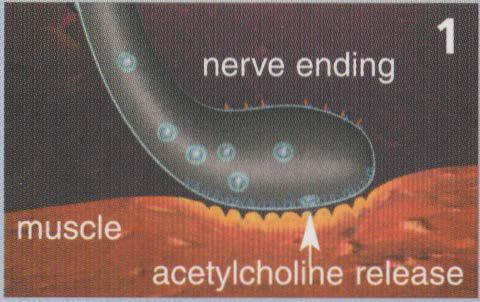
Figure 1: At the normal neuromuscular junction a nerve impulse triggers the release of acetylcholine, which causes muscles to contract. Excessive release of acetylcholine causes overactive muscle contractions and muscle spasms.
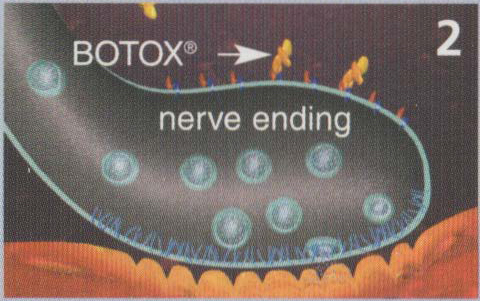
Figure 2: Botulinum toxin is effective in reducing this activity. Once injected, botulinum toxin binds to the nerve terminal.

Figure 3: Botulinum toxin blocks the release of acetylcholine, relaxing overactive muscles.
How does botulinum toxin manage blepharospasm?
Botulinum toxin reduces both the strength and frequency of eyelid muscle contractions and therefore reduces the symptoms of blepharospasm. The effect of Botulinum toxin is not permanent, but usually lasts between 3 and 6 months. A low dose of botulinum toxin is used initially, and in most people that level is sufficient to provide relief of symptoms. Your doctor can adjust the dose of botulinum toxin as well as the time interval between injections based on your response to treatment. Usually, once an appropriate dose of botulinum toxin has been determined, the dose and time interval between injections will be constant for further treatments. People often know when the beneficial effects of botulinum toxin treatment subside and that another course of treatment is required.
How does Botulinum toxin manage hemifacial spasm?
As with blepharospasm, botulinum toxin reduces both the strength and frequency of contractions of the affected muscles and therefore reduces the symptoms of hemifacial spasm. In addition to injections around the eye, injecting the region around the mouth may be enough to stop any lower face movement. If not, cheek muscles can also be injected.
How is botulinum toxin given?
Botulinum toxin is given by injection. The volume administered in each injection is very small – typically 0.1 ml or less – and is injected with a fine needle into the muscles around the eye and/or face that are causing the increased blinking or spasms. The number and location of injections can be altered depending on the success of initial treatment. Your doctor may vary the injection technique in order to optimise your treatment outcome. Figures 1 and 2 illustrate the possible injection sites for blepharospasm and hemifacial spasm.
Like all injections, there is some discomfort and it is commonly described as being like an ant bite. Placing a cold pack over the area for injection prior to, and after, treatment may help minimise the discomfort.
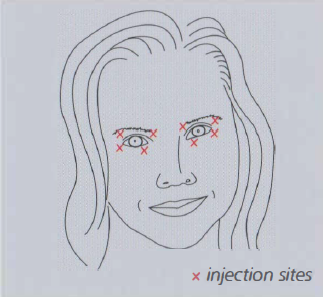
Figure 1: Typical injection sites for blepharospasm.
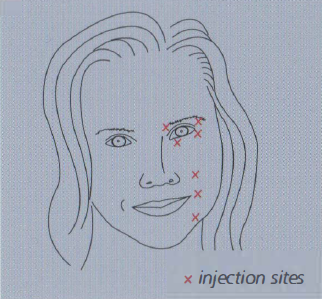
Figure 2:Typical injection sites for hemifacial spasm. Sites will vary from person to person.
How long can I be treated with botulinum toxin?
Treatments can be repeated as long as your condition responds to botulinum toxin and you do not have any serious allergic reactions or other significant side effects to the treatment.
Although most people continue to respond to botulinum toxin, some people have experienced a diminished response over time. This could be caused by changes in the condition. Identifying and injecting the affected muscle can be difficult and is complicated by the changing pattern of muscle involvement and progression of the disorder. If the pattern of muscle activity changes, new affected muscles may need to be treated and/or a change in dose may be required.
Expectations of treatment can also change over time. It may appear that the first botulinum toxin injection was more helpful than subsequent injections. This may be because the condition was quite severe when the first injection was given. Subsequent injections are usually given before the condition becomes that severe again. Therefore, the relief experienced with subsequent injections may not seem as dramatic as first time.
Dr Hollenbach has been accredited for therapeutic use of botulinum toxin in the specific treatment of blepharospasm and hemifacial spasm. He is the only ophthalmologist, ophthalmic surgeon, or oculoplastic surgeon in Newcastle to be registered for the therapeutic use of botulinum toxin and has been doing botulinum toxin injections for patients with these afflictions for more than 20 years.
BOOK AN APPOINTMENT WITH US
To find out if this treatment is right for you.
